Neuromechanics
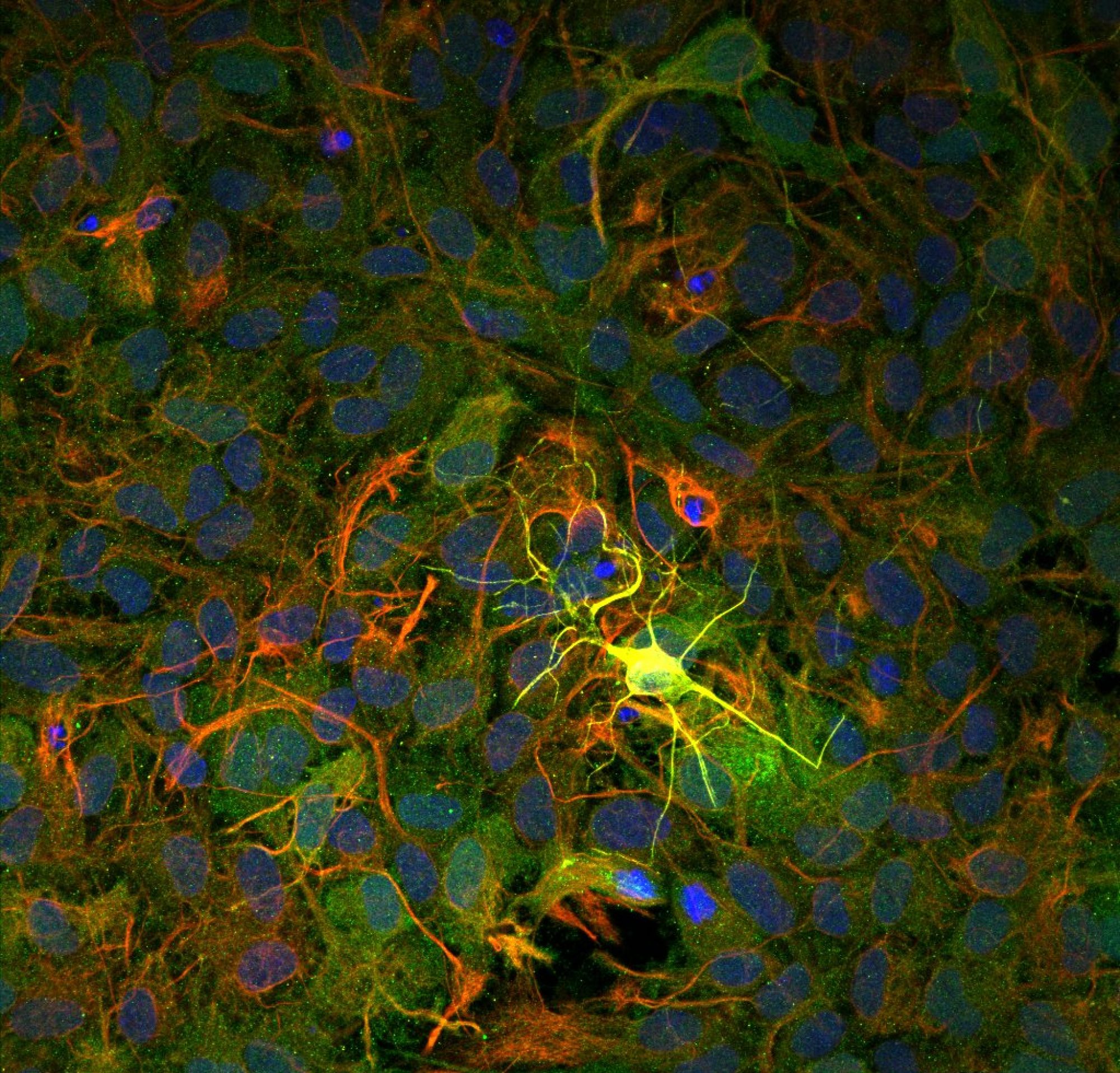
Neuron cells are responsible for memory, learning and intelligence in animals. Neurons form neuron-neuron or neuro-muscular junctions, called synapses. They exchange information at the synapse by firing (neuro-transmission), using neurotransmitters. During firing, neurotransmitters are released from vesicles that are clustered at the synapse. It has long been understood that vesicle clustering is mediated by biochemical processes in neurons. We found, to our surprise, that neurons generate mechanical tension after forming synapses, and that vesicle clustering depends on the mechanical tension. Clustering vanishes upon releasing neuronal tension by severing the neuron, but is restored when mechanical tension is applied to the severed end. We are addressing the following questions: (1) How neuron tension is linked with vesicle clustering? (2) What is the origin of tension?